#非结构化文本数据的分析解决方案
在处理大量非结构化文本数据时,传统的数据标注方法往往依赖于已知的分类清单。 然而,在许多实际应用场景中,我们可能没有一个明确的分类清单。 这时,利用大模型进行文本聚类就显得尤为重要,它可以作为分类任务的前置环节,帮助我们将非结构化的文本反馈转化为结构化的、可分析的数据。
#项目介绍及实现流程
#项目流程图
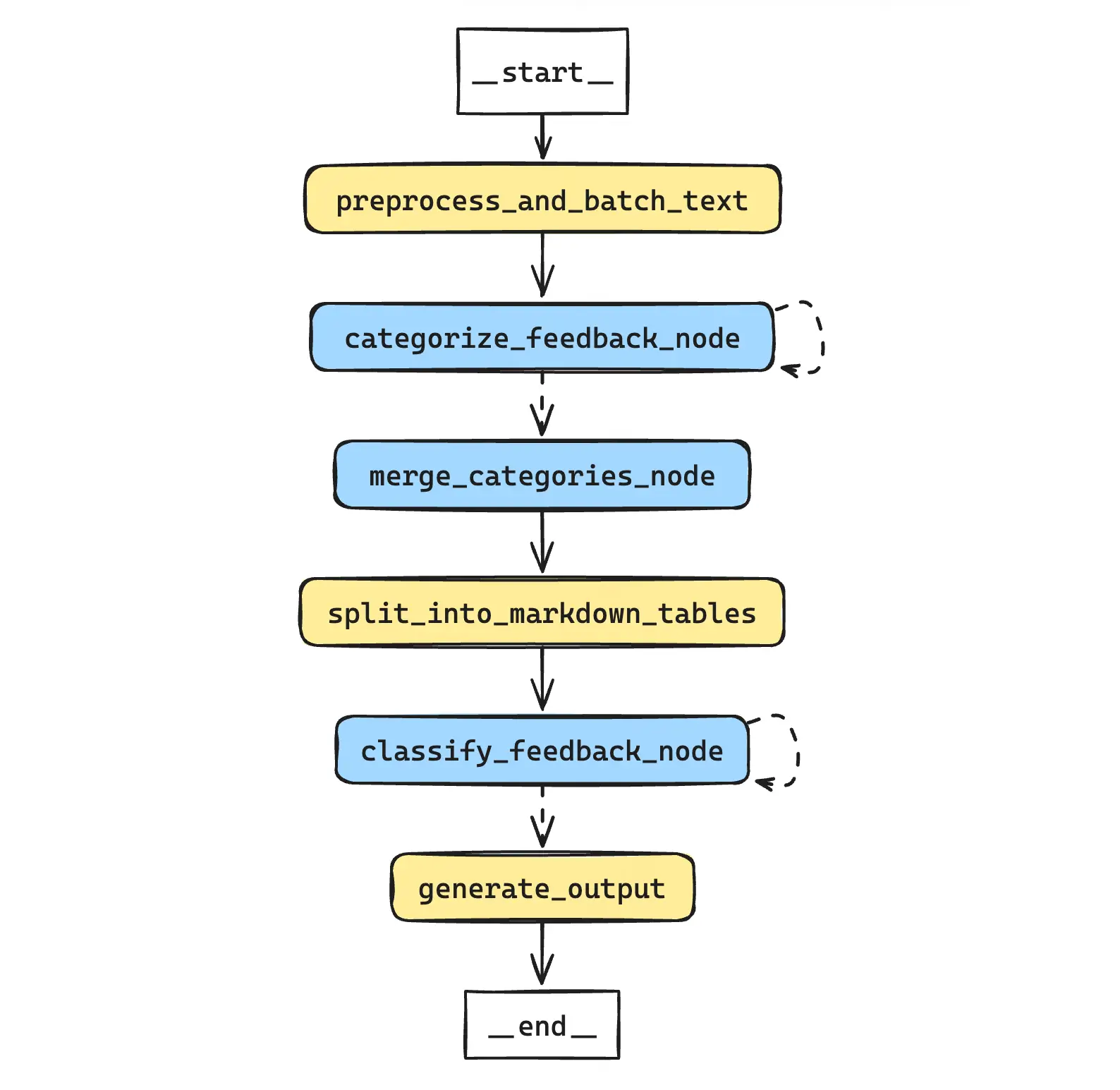
项目的核心目标是将非结构化的文本反馈转化为结构化的、可分析的数据。实现过程主要包括以下几个关键步骤:
-
数据预处理与分块:
- 对原始反馈数据进行清洗和标准化。
- 考虑到大模型的上下文窗口限制,将文本数据按字符数量进行分块。
-
主题聚类:
- 利用大模型对每个数据批次进行主题聚类。
- 通过迭代方式处理所有数据批次,确保全面覆盖。
-
主题整合:
- 对多批次的聚类结果进行整合和优化。
- 消除重复类别,合并相似主题,确保分类方案的全面性和精确性。
-
数据集切分:
- 将处理后的数据转换为Markdown格式的表格。
-
分类任务:
- 基于优化后的分类方案,对每条员工反馈进行逐条分类。
-
生成最终输出:
- 整合原始反馈和对应分类,生成结构化的结果数据,供后续统计分析。
#代码实现
#准备工作
#导入依赖
导入依赖与上一个数据清洗的案例基本一致,在此省略。
#案例数据集
案例中使用的文本数据集,采用Kaggle上的公开数据集Attrition Based on Accenture Review's 2021,这是一个包含了员工反馈文本的数据集。
#构建任务
#GraphState
class FeedbackClassificationState(TypedDict):
"""
用于管理反馈分类的状态。
"""
raw_feedback_data: pd.DataFrame
batched_texts: List[List[str]]
classification_results_list: List[Dict]
merged_categories: Dict
markdown_tables: List[str]
feedback_classification_results: List[Dict]
final_output: pd.DataFrame
batch_index: int
total_batches: int
classification_batch_index: int
total_classification_batches: int#数据分块
在这个阶段,我们首先对原始文本进行清洗,包括去除特殊字符、统一格式等。 然后,考虑到大模型的输入限制,我们需要将长文本分割成适当大小的块。这里我们采用了基于字符数的分块策略,同时确保每个块的语义完整性。
关键技术点:
- 使用正则表达式进行文本清洗
- 实现动态分块算法,平衡块大小和语义完整性
- 随机打乱数据,提高样本多样性,避免类似内容集中在一起
def preprocess_and_batch_text(state: Dict) -> Dict:
import re
import random
input_dataset = state['raw_feedback_data']
batch_char_limit = 700
seed = 94
random.seed(seed)
def preprocess_text(text):
pattern = r"['‘’""“”{}]"
replacement = '`'
if isinstance(text, str):
return re.sub(pattern, replacement, text)
return ''
def count_words(text):
chinese_char_count = len(re.findall(r'[\u4e00-\u9fff]', text))
english_word_count = len(re.findall(r'\b[a-zA-Z]+\b', text))
return chinese_char_count + english_word_count
input_dataset.loc[:, 'pros'] = input_dataset['pros'].apply(preprocess_text)
input_dataset.loc[:, 'cons'] = input_dataset['cons'].apply(preprocess_text)
all_texts = input_dataset['pros'].tolist() + input_dataset['cons'].tolist()
random.shuffle(all_texts)
batches = []
current_batch = []
current_batch_char_count = 0
for text in all_texts:
text_char_count = count_words(text)
if current_batch_char_count + text_char_count > batch_char_limit and current_batch:
batches.append(current_batch)
current_batch = []
current_batch_char_count = 0
current_batch.append(text)
current_batch_char_count += text_char_count
if current_batch:
batches.append(current_batch)
state['batched_texts'] = batches
state['total_batches'] = len(batches)
state['batch_index'] = 0
state['classification_results_list'] = []
return state#主题聚类
主题聚类是本项目的核心步骤之一。我们利用大模型的强大语义理解能力,对每个数据批次进行无监督的主题发现。
技术要点:
- 设计专门的提示模板,引导模型进行主题识别和分类
- 使用Pydantic模型定义输出格式,确保结果的一致性和可解析性
- 实现批次处理逻辑,有效管理大规模数据集
class FeedbackCategory(BaseModel):
id: int = Field(..., description="Category ID starting from 1.")
name: str = Field(..., description="Concise and clear label for the category.")
description: str = Field(..., description="Detailed description differentiating the category from others.")
class FeedbackCategories(BaseModel):
categories: List[FeedbackCategory] = Field(..., description="List of categorized themes in the feedback.")
system_message = """
你是一位文本挖掘和分类专家。你的任务是深入分析员工的反馈内容,并将反馈中涉及的主题按照以下原则进行分类:
1. 分类原则:
- 互斥:确保每个类别之间相互独立,没有重叠或交集。
- 具体:类别应明确、清晰,避免模糊不清的分类。
- 有意义:类别应具有普遍性,能涵盖多数相关的员工反馈。
2. 分类要求:
- 使用中文进行分类。
- 类别数量不超过10个。
- 类别名称应简洁、准确,一目了然地反映核心主题。
- 类别描述应详尽、清晰,阐述该类别所包含的内容,并与其他类别区分。
3. 分类策略:
- 全面覆盖原始数据中所有主要主题。
- 避免创建过多类别,可将较少出现的主题合并到"其他"类别。
- 忽略质量不高或内容不清晰的反馈。
请严格遵循这些原则和要求,确保分类结果的准确性和实用性。
"""
format_instructions = """
Output your answer as JSON that matches the given schema: ```json\n{schema}\n```. Make sure to wrap the answer in ```json and ``` tags. No need to repeat the schema.
"""
human_message_template = """
请根据以下员工反馈内容进行分析,严格遵循系统消息中的分类原则、要求和策略,使用中文对反馈内容进行分类。
分析步骤:
1. 仔细阅读并理解所有员工反馈。
2. 识别反馈中的主要主题和关键词。
3. 根据主题的相似性和重要性进行初步分类。
4. 检查并调整分类,确保符合所有要求。
5. 为每个类别创建简洁的名称和详细的描述。
员工反馈内容:
{feedback_text}
请提供符合指定JSON格式的分类结果。
"""
parser = PydanticOutputParser(pydantic_object=FeedbackCategories)
prompt_template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", system_message + format_instructions),
("human", human_message_template),
]
).partial(schema=FeedbackCategories.schema())
categorize_feedback = prompt_template | language_model | parserdef categorize_feedback_node(state: Dict) -> Dict:
batch_index = state['batch_index']
batched_texts = state['batched_texts']
feedback_text = batched_texts[batch_index]
result = categorize_feedback.invoke({"feedback_text": feedback_text})
state['classification_results_list'].append(result.dict())
state['batch_index'] += 1
return state#determine_next_step
def determine_next_step(state: Dict) -> str:
if state['batch_index'] < state['total_batches']:
return "categorize_feedback_node"
else:
return "merge_categories_node"#主题整合
在完成初步聚类后,我们需要对多个批次的结果进行整合。这个过程不仅仅是简单的合并,还涉及到类别的重新评估和优化。
class FeedbackCategory(BaseModel):
id: int = Field(..., description="Category ID starting from 1.")
name: str = Field(..., description="Concise and clear label for the category.")
description: str = Field(..., description="Detailed description differentiating the category from others.")
class FeedbackCategories(BaseModel):
categories: List[FeedbackCategory] = Field(..., description="List of categorized themes in the feedback.")
system_message = """
你是一位精通数据整合和主题分类的专家。你的任务是分析多个批次的员工反馈分类结果,并将它们整合为一个全面、精确的最终分类方案。
你的主要职责包括:
1. 分析和比较不同批次的分类结果。
2. 识别重复、相似或重叠的类别。
3. 合并相关类别,确保最终类别之间互斥且有明确界限。
4. 重新评估和调整类别名称和描述,确保它们准确、简洁且具有代表性。
5. 确保最终的分类方案全面覆盖所有重要主题,同时保持类别数量在合理范围内(不超过15个)。
在整合过程中,请遵循以下原则:
- 保持中文作为输出语言。
- 确保类别之间相互独立,没有重叠。
- 类别名称应简洁明了,类别描述应详细且有区分性。
- 保持客观性,避免主观判断。
- 对于频率较低的主题,考虑是否值得单独成类或合并到其他类别。
- 最终的分类方案应具有普遍适用性,能够涵盖大多数员工反馈。
请仔细分析输入的所有分类结果,综合考虑各个批次的特点,创建一个最优的、统一的分类方案。
"""
human_message_template = """
以下是多个批次的员工反馈分类结果,将这些结果整合为一个全面、精确的最终分类方案。
分类结果:
{classification_results}
请按照以下步骤进行整合:
1. 仔细阅读并分析所有批次的分类结果。
2. 识别各批次中重复、相似或重叠的类别。
3. 合并相关类别,确保最终类别之间互斥且有明确界限。
4. 重新评估并优化类别名称和描述。
5. 检查是否有遗漏的重要主题,必要时添加新类别。
6. 确保最终的分类方案全面且类别数量合理(建议在10-15个之间)。
请提供符合指定JSON格式的最终整合分类结果。
"""
parser = PydanticOutputParser(pydantic_object=FeedbackCategories)
prompt_template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", system_message + format_instructions),
("human", human_message_template),
]
).partial(schema=FeedbackCategories.schema())
merge_categories = prompt_template | language_model | parserdef merge_categories_node(state: Dict) -> Dict:
classification_results_list = state['classification_results_list']
classification_results = [FeedbackCategories.parse_obj(result).dict() for result in classification_results_list]
result = merge_categories.invoke({"classification_results": classification_results})
state['merged_categories'] = result.dict()
return state#数据分块为Markdown表格
为了便于后续的分类任务,我们将处理后的数据转换为Markdown格式的表格,适合作为模型的输入。
def split_into_markdown_tables(state: Dict) -> Dict:
data = state['raw_feedback_data']
columns = ['index', 'pros']
n = 10
data = data.dropna(subset=columns, how='any')
text_columns = [col for col in columns if data[col].dtype == 'object']
for col in text_columns:
data[col] = data[col].str.replace('\r\n', ' ', regex=True)
df = data[columns]
markdown_tables = []
for start in range(0, len(df), n):
subset = df.iloc[start:start + n]
markdown_table = "| " + " | ".join(columns) + " |\n"
markdown_table += "| " + " | ".join(["---"] * len(columns)) + " |\n"
for index, row in subset.iterrows():
row_values = [str(row[col]) for col in columns]
markdown_table += "| " + " | ".join(row_values) + " |\n"
markdown_tables.append(markdown_table)
state['markdown_tables'] = markdown_tables
state['total_classification_batches'] = len(markdown_tables)
state['classification_batch_index'] = 0
state['feedback_classification_results'] = []
return state#分类任务
在这个阶段,我们使用优化后的分类方案对每条员工反馈进行分类。
class FeedbackOutput(BaseModel):
id: str = Field(..., description="Corresponding employee feedback ID from input")
category: str = Field(..., description="Feedback category based on predefined classification")
class FeedbackClassification(BaseModel):
classifications: List[FeedbackOutput] = Field(..., description="List of classification results for all feedbacks")
system_message = """
你是一位文本分类专家。你的任务是根据预定义的分类规则,对给定的员工反馈进行主题分类。请遵循以下指南:
1. 分类规则:
{categories}
2. 分类要求:
- 仔细阅读每条反馈,理解其核心内容。
- 根据反馈内容,从预定义的类别中选择最合适的一个。
- 如果一条反馈涉及多个主题,选择最主要或最突出的一个。
- 如果反馈内容不清晰或不属于任何预定义类别,将其归类为"其他"。
3. 输出格式:
- 对每条反馈,输出其ID和对应的类别。
- 严格遵循指定的JSON格式。
请确保分类的一致性和准确性,不要遗漏任何反馈。
"""
human_message_template = """
请对以下员工反馈进行分类。输入数据为Markdown格式的表格,包含ID和反馈文本两列。
员工反馈:
{feedback_table}
请按照系统消息中的指南进行分类,并以指定的JSON格式输出结果。
"""
parser = PydanticOutputParser(pydantic_object=FeedbackClassification)
prompt_template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", system_message + format_instructions),
("human", human_message_template),
]
).partial(schema=FeedbackClassification.schema())
classify_feedback = prompt_template | language_model | parserdef classify_feedback_node(state: Dict) -> Dict:
classification_batch_index = state['classification_batch_index']
markdown_tables = state['markdown_tables']
merged_categories = state['merged_categories']
feedback_table = markdown_tables[classification_batch_index]
result = classify_feedback.invoke({"feedback_table": feedback_table, "categories": merged_categories})
state['feedback_classification_results'].append(result.dict())
state['classification_batch_index'] += 1
return state#determine_classification_next_step
def determine_classification_next_step(state: Dict) -> str:
if state['classification_batch_index'] < state['total_classification_batches']:
return "classify_feedback_node"
else:
return "generate_output"#生成最终输出
最后,我们将分类结果与原始数据整合,生成最终的结构化输出。这个输出不仅包含原始反馈,还包括对应的分类标签。
def generate_output(state: Dict) -> Dict:
feedback_classification_results = state['feedback_classification_results']
final_output_list = []
for batch_result in feedback_classification_results:
for classification in batch_result['classifications']:
final_output_list.append({
'id': classification['id'],
'category': classification['category']
})
final_output_df = pd.DataFrame(final_output_list)
# 拼接回原始数据集
raw_feedback_data = state['raw_feedback_data']
final_output_df = raw_feedback_data.merge(final_output_df, on='id', how='left')
state['final_output'] = final_output_df
return state#构建流程图
workflow = StateGraph(FeedbackClassificationState)
workflow.add_node("preprocess_and_batch_text", preprocess_and_batch_text)
workflow.add_node("categorize_feedback_node", categorize_feedback_node)
workflow.add_node("merge_categories_node", merge_categories_node)
workflow.add_node("split_into_markdown_tables", split_into_markdown_tables)
workflow.add_node("classify_feedback_node", classify_feedback_node)
workflow.add_node("generate_output", generate_output)
# 构建流程图
workflow.set_entry_point("preprocess_and_batch_text")
workflow.add_edge("preprocess_and_batch_text", "categorize_feedback_node")
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"categorize_feedback_node",
determine_next_step,
{
"categorize_feedback_node": "categorize_feedback_node",
"merge_categories_node": "merge_categories_node"
}
)
workflow.add_edge("merge_categories_node", "split_into_markdown_tables")
workflow.add_edge("split_into_markdown_tables", "classify_feedback_node")
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"classify_feedback_node",
determine_classification_next_step,
{
"classify_feedback_node": "classify_feedback_node",
"generate_output": "generate_output"
}
)
workflow.add_edge("generate_output", END)
# 编译流程图
app = workflow.compile()#效果演示
由于该任务的数据量较大,输入输出和保存在 state 中的信息无法在博客中展示,因此放一下在执行任务过程,在 langgraph 中的监控流程。
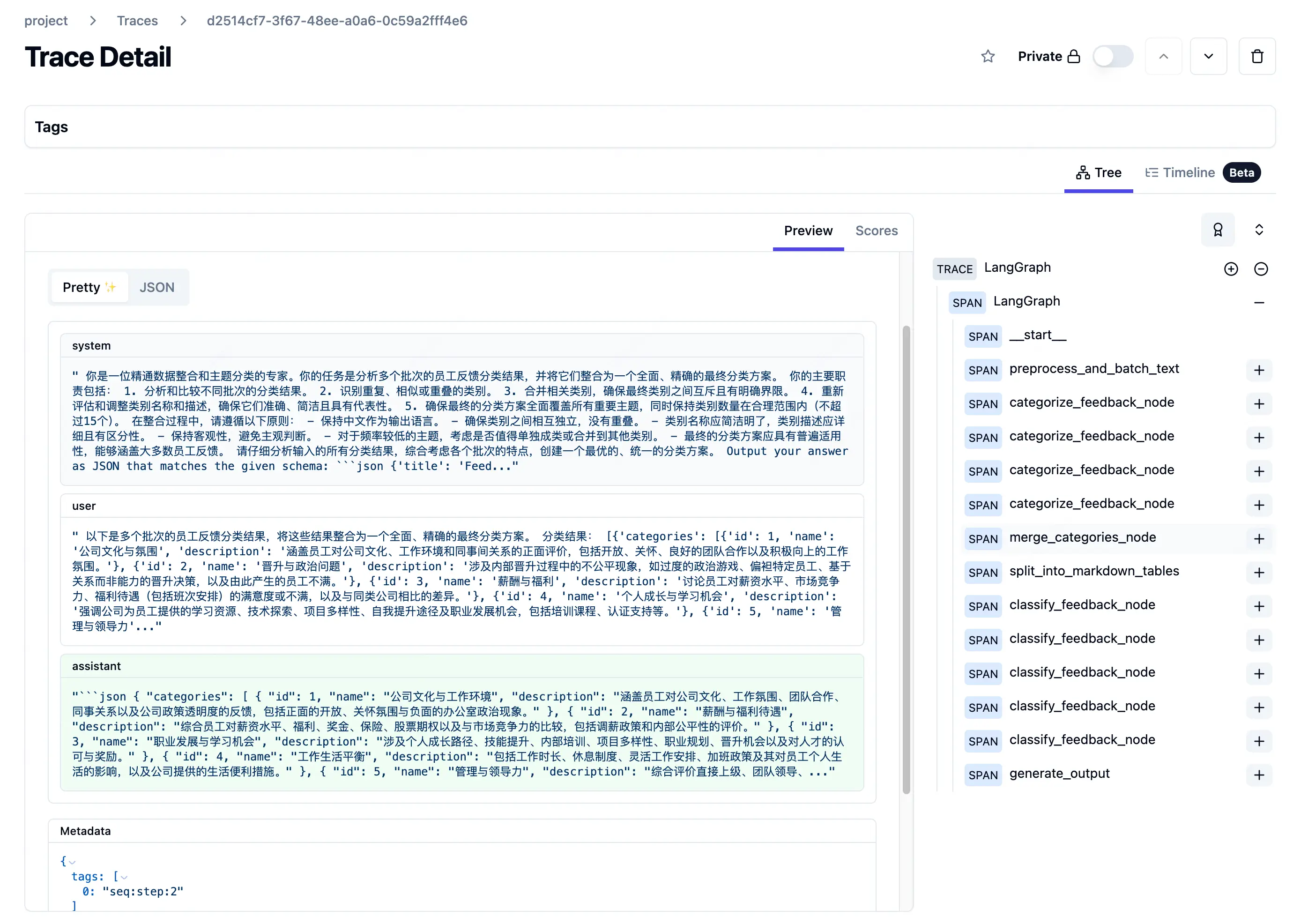
可以看到,主题聚类的任务循环了 4 次,而数据标注的任务迭代了 5 次完成。
#结论
本项目展示了如何利用大型语言模型进行文本聚类和分类,为非结构化文本数据的分析提供了一个强大而灵活的解决方案。 通过结合大模型的语义理解能力和传统的数据处理技术,我们能够更有效地从文本数据中提取有价值的见解。